Fitts’ Law demonstrates how to ease interactions through the careful sizing and positioning of interface elements. It states: The time it takes to acquire a target is a function of the distance to and size of the target. It is particularly important when designing buttons and other clickable on-screen elements.
1. Size
When an entire button is large, clickable, and has clear boundaries, they’re easy to select. Users can intuitively understand where to click and where not to click. But forcing users to point their cursor directly over a specific part of a button, like the text, requires more precision and time. But bigger isn’t always better. Buttons that are large enough to demand attention without disrupting the visual balance of your page are what maximize usability.
2. Distance
When users land on the website, and you want them to take a specific action, you need to estimate where the starting point of their cursor will be. This is called the prime pixel. It allows building a consistent and easy-to-navigate site and creates the shortest path to the desired CTA. For instance, Google’s search box is always in the center of the screen because when users enter the site, they’re most likely looking at the middle of the screen. Most of the time, the prime pixel should influence the location of the target object. And the shorter the path to the desired action, the better the user experience.
3.Effort
A lot of vital commands like ‚exit‘, ’start‘, and ’shut down‘ are located in the corners of your computer screen. Placing buttons there makes it easier for users to select them because the buttons are pinned by two sides. And the cursor stops at each side, so you can’t go beyond them. This means you don’t have to be as precise when you want to click a button in a corner or edge. You just have to move your cursor to its general vicinity.
It’s always important to test assumptions. I found an online software where it’s easy to check it. http://fww.few.vu.nl/hci/interactive/fitts/
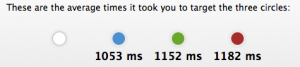
- Al circles are of the same size and in equal distance to target.
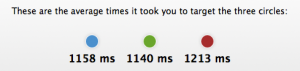
- Circles are still the same but the most distant takes the longest to target.
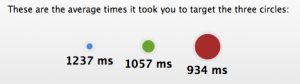
- Circles are different sizes but in equal distance. It proves that biggest objects are easier to aim.
- Fitt’s law. https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/fitts-law
- Test programe http://fww.few.vu.nl/hci/interactive/fitts/
- The importance of size and distance in UI design https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/fitts-s-law-the-importance-of-size-and-distance-in-ui-design
